This is the final part of the article. Here we see the motivation theories. Here you find the
first part.
MOTIVATIONAL THEORIES
- Abraham Maslow’s “Hierarchy of needs theory”.
- Frederick Herzberg’s “Two factors theory” (motivation-hygiene theory)
- Claton P. Aldafar’s “ERG theory”
- MC Gregor’s “X” and “Y” theory.
- J.K. Atkinson and David C. MC Clelland’s “Need theory of Motivation”
- Viktor E Frankl’s “Will to meaning theory”
- B.F. Skineer’s “Conditioning and Reinforcement theory”.
- Victor H. Vroom’s “Expectancy theory”.
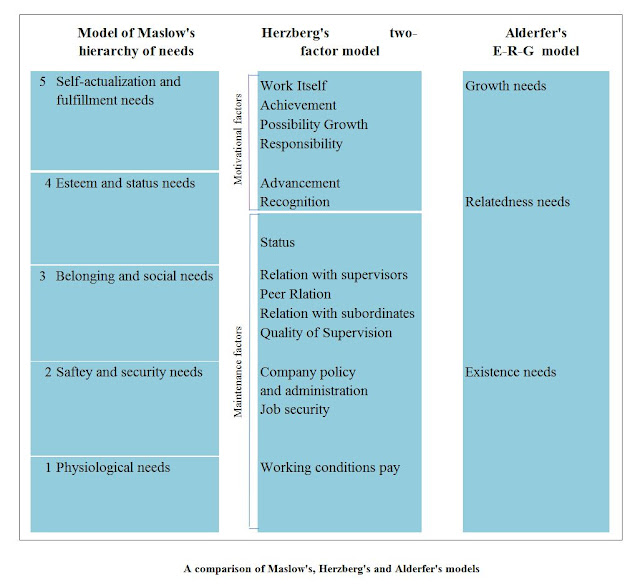
ABRAHAM MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS THEORY
 |
| Abraham Maslow's Hierachy of Needs Theory |
Physiological need or Biological Need: Hunger, thirst, sex, air, food, water and so on. (Bodily need
fulfillment)
Safety needs: Protection against danger, threat, deprivation and
so on.
Social Needs: Belonging, association, acceptance by others, giving and receiving friendship and love.
Ego or Esteem Needs: Self esteem (Self confidence, independence, achievement, competence,
knowledge) and personal reputation (status recognition appreciation respect).
Self actualization or self fulfillment Need: Realizing one’s own potential, continued self development, creativity.
CRITICAL FACTORS TOR TAKING BEHAVIORAL DECISIONS
- Net profit: Observed value of the reward minus observed cost of the reward.
- Cost of failing: Cost of trying plus penalties for failing.
- Perceived probability of success
- Confidence in calculation.
According to behavioral scientist another point is Emotions. This is the most powerful force that motivate us even if they are not particularly rational.
What is Emotion ?
An Emotion may be defined as a stirred –up – state of the mind accompanied by the physiological changes.
Emotions result from need seeking activities and are, therefore, indirect cause of behavior.
Most human behavior has a motivational base which seeks to satisfy needs.
If an operating manager is to try to draw some level of activity from a subordinate, he must have an understanding or awareness of the specific human needs that must be satisfied if the stirred –up –state is to be eliminated.
Two- Factor Theory:
Herzberg categorized those variables directly related to motivation and those not directly related, which he called hygiene factors.
Motivation
Achievement recognition work itself responsibility advancement
Hygiene factors
Company policy pay working conditions supervision benefits.
Victor H.Vroom’s-Expectancy Theory:
Motivation is a product of three factors: How much one wants a reward(valance), one’s estimate of the probability that effort will result in successful performance(expectancy), and one’s estimate that performance will result in receiving the reward(Instrumentality). This relationship is stated in the following formula:
Motivation = Valence x Expectancy x Instrumentality
The three factors
Valence: Valence refers to the strength of person’s preference for receiving a reward. It is an expression of the amount of one’s desire to reach a goal.
Expectancy: Expectancy is the strength of belief that one’s work-related effort will result in completion of a task.
For example- a person selling a magazine subscriptions door-to-door may know from experience that volume of sales is directly related to the number of sales call made. Expectancies are stated as probabilities.
Instrumentality: Instrumentality represents the employees belief that a reward will be received once the task is accomplished. Here the employee makes another subjective judgment about the probability.
J.K.Atkinson & David C.Mc-Clelland
According to them the individual personality is assumed to be composed of a network of three basic motives.
- The need for achievement.
- The need for affiliation.
- The need for power.
- It is possible to think of specific type of behavour that are likely to be associated with each kind of motive.Mc. Clelland found that people with high need to achieve tend to
- 1.Seek and assumed high degree of personal responsibility
- Take calculated risk
- Set challenging but realistic goals for themselves.
- Develop comprehensive plans to help them achieve their goals.
- Seek and use concrete measurable feed back of the results of their actions
- Seek out business opportunities where their desire to achieve will not be thwarted.
Viktor E Frankl
The first two analytical motivational model dealt with the idea of motives and the type of motivated behaviour that manager may apply to other people. Frankl in his book Men’s search for meaning writes more directly to individual person and his own motivation. Frankl, believes, for example, that a great deal of man’s basic frustration from his inability to find what Frankl calls the “Will to meaning” . He believes that a people have a basic need to do meaningful things, and thus when put into an environment that does not allow for meaning people become frustrated and develop neurotic behavior.
Clayton Alderfer’s E-R-G model
Clayton Alderfder proposed a modified need hierarchy-the E-R-G model with just 3 levels. He suggested that employees are initially interested in satisfying their existence needs, which combine physiological and security factors. Pay, physical working conditions, job security, and frienge benefits. Can all address these needs. Relatedness needs are at the next level. And these involve being understood and accepted by the people above, below and around the empolyee at work and away from it.
Growth needs are in the 3rd category, these involve the desire for both self esteem and self actualization.






.jpg)












